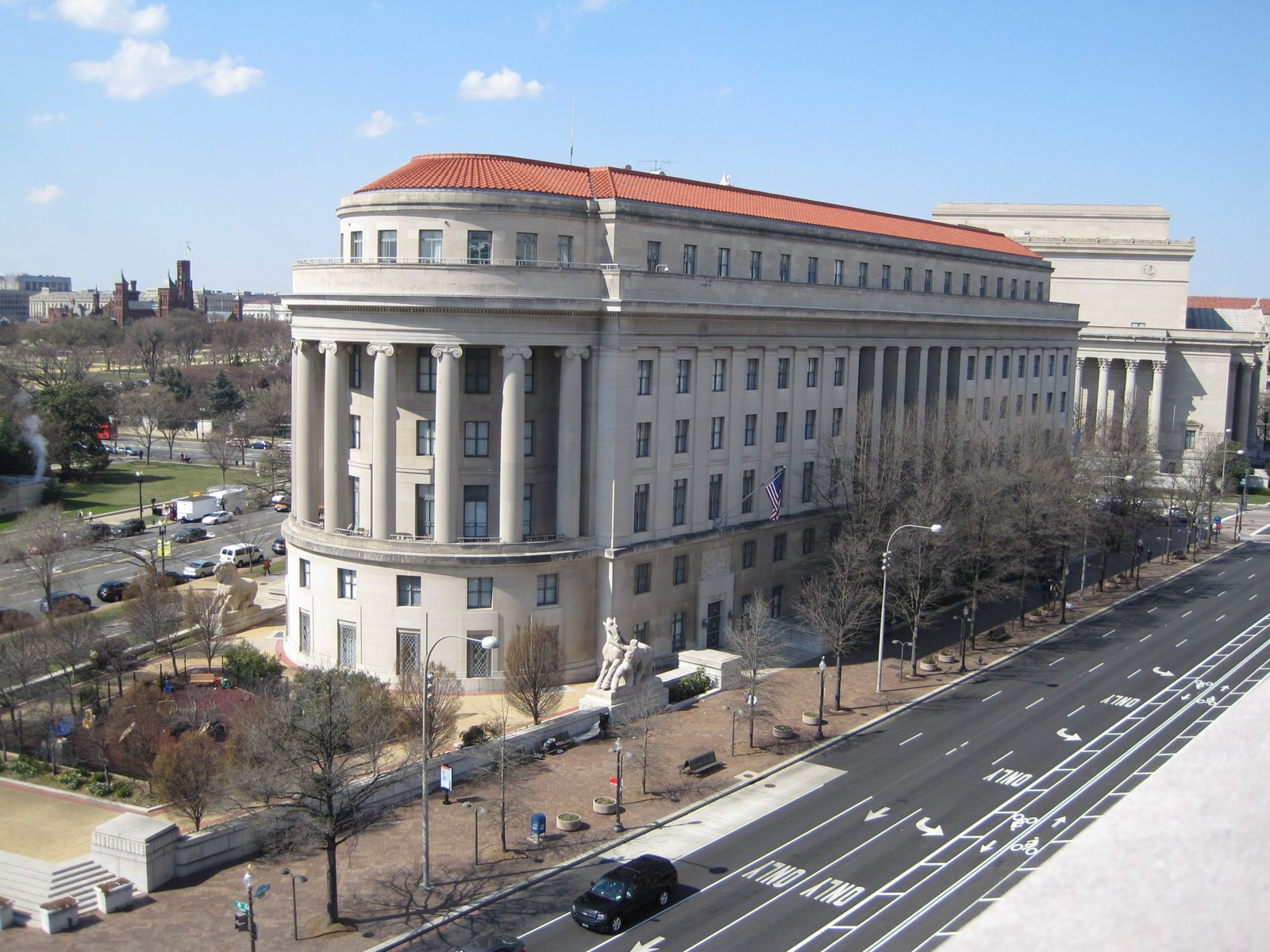
FTC is an independent agency of the United States government, established to protect consumers and promote fair competition in the marketplace. The creation of the FTC can be traced back to the early 20th century.
In response to growing concerns about unfair business practices and monopolistic behavior by large corporations, the Federal Trade Commission Act was signed into law on September 26, 1914, by President Woodrow Wilson. This act established the FTC as a regulatory body with the authority to investigate and take action against deceptive and anticompetitive practices.
The main purpose of the FTC is to prevent unfair methods of competition and deceptive acts or practices that could harm consumers or undermine competition. It has the authority to enforce a wide range of laws, including the Federal Trade Commission Act, the Clayton Antitrust Act, and the Robinson-Patman Act.
Over the years, the FTC has played a crucial role in safeguarding consumer rights and maintaining a level playing field in the marketplace. It has taken action against numerous companies engaged in deceptive advertising, unfair pricing, and anticompetitive behavior.
Today, the FTC continues to adapt to the changing landscape of the digital economy, addressing issues such as online privacy, data security, and emerging technologies. It works in collaboration with other government agencies and international counterparts to ensure consumer protection and fair competition.
In conclusion, the FTC was created in 1914 through the Federal Trade Commission Act to protect consumers and promote fair competition. Its establishment marked a significant milestone in the history of consumer rights and antitrust regulation in the United States.